Tutorial for sorting data stored as numpy to on-resonance R1rho analysis
Revision as of 22:53, 14 November 2015 by Troels Emtekær Linnet (talk | contribs) (→Create data files for relax)
Data background
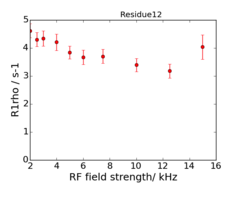
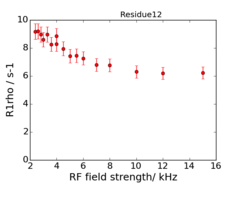
This is data recorded at 600 and 950 MHz.
For each spectrometer frequency, the data is saved in np.arrays
- one for the residue number,
- one for the rates,
- one for the errorbars,
- one for the RF field strength.
They can be retrieved also with scipy's loadmat command.
The experiments are on-resonance R1rho, and the rates are already corrected for the (small) offset effect, using the experimentally determined R1.
Specifically, the numpy shapes of the data is:
- For 600 MHz
- residues (1, 60)
- rates (60, 10)
- errorbars_rate (60, 10)
- RFfields (1, 10)
- For 950 Mhz
- residues (1, 61)
- rates (61, 19)
- errorbars_rate (61, 19)
- RFfields (1, 19)
An example of the data at the 2 fields is:
Create data files for relax
First prepare data, by running in python.
python 1_prepare_data.py
File: 1_prepare_data.py
import os
import scipy as sc
import scipy.io
import numpy as np
# Set path
cwd = os.getcwd()
fields = [600, 950]
file_names = ['residues', 'rates', 'errorbars_rate', 'RFfields']
# Store data in dictionary
all_data = {}
all_data['fields'] = fields
all_data['file_names'] = file_names
# Make list of residues and make unique
all_res = []
# Loop over the experiments, collect all data
for field in fields:
print "\n", field
# Make a dic inside
all_data['%s'%field] = {}
# Construct the path to the data
path = cwd + os.sep + "Archive" + os.sep + "exp_%s"%field + os.sep + "matrices" + os.sep
all_data['%s'%field]['path'] = path
# Collect all filename paths
field_file_name_paths = []
for file_name in file_names:
# Create path name
file_name_path = path + "%s.mat"%file_name
field_file_name_paths.append(file_name_path)
# Load the data
file_name_path_data = sc.io.loadmat(file_name_path)
# Extract as numpy
file_name_path_data_np = file_name_path_data[file_name]
# And store
all_data['%s'%field]['%s'%file_name] = file_name_path_data
all_data['%s'%field]['np_%s'%file_name] = file_name_path_data_np
print file_name, file_name_path_data_np.shape
# Collect residues
if file_name == "residues":
all_res += list(file_name_path_data_np.flatten())
# Store
all_data['%s'%field]['field_file_name_paths'] = field_file_name_paths
# Make list of residues and make unique
all_res_uniq = sorted(list(set(all_res)))
all_data['all_res_uniq'] = all_res_uniq
# Write a sequence file for relax
f = open("residues.txt", "w")
f.write("# Residue_i\n")
for res in all_res_uniq:
f.write("%s\n"%res)
f.close()
f_exp = open("exp_settings.txt", "w")
f_exp.write("# sfrq_MHz RFfield_kHz file_name\n")
# Then write the files for the rates
for field in all_data['fields']:
resis = all_data['%s'%field]['np_residues'][0]
rates = all_data['%s'%field]['np_rates']
errorbars_rate = all_data['%s'%field]['np_errorbars_rate']
RFfields = all_data['%s'%field]['np_RFfields'][0]
print "\nfield: %3.3f"%field
for i, RF_field_strength_kHz in enumerate(RFfields):
#print "RF_field_strength_kHz: %3.3f"%RF_field_strength_kHz
# Generate file name
f_name = "sfrq_%i_MHz_RFfield_%1.3f_kHz.in"%(field, RF_field_strength_kHz)
cur_file = open(f_name, "w")
cur_file.write("# resi rate rate_err\n")
exp_string = "%11.7f %11.7f %s\n"%(field, RF_field_strength_kHz, f_name)
print exp_string,
f_exp.write(exp_string)
for j, resi in enumerate(resis):
rate = rates[j, i]
error = errorbars_rate[j, i]
string = "%4d %11.7f %11.7f\n"%(resi, rate, error)
cur_file.write(string)
cur_file.close()
f_exp.close()